补完一套题。
题目链接
B Integer Coords
题意是给出选取点的$X、Y$的范围,在里面选取$2$个点,需要这两个点连起来的线段具有$K$个整数点。问有多少种选取方法。
两个点$(x1,y1),(x2,y2)$连起来的线段具有的整数点的数量为 $gcd(abs(x1-x2),abs(y1-y2)) + 1$。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| int n;
void solve()
{
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
int ans = 0;
repp(i1, 0, n)
{
repp(j1, 0, m)
{
repp(i2, i1, n)
{
repp(j2, (i2==i1?j1:0), m)
{
int d1 = abs(i1 - i2);
int d2 = abs(j1 - j2);
int cnt = 0;
if (d1 == 0)
{
cnt = d2 + 1;
}
else if (d2 == 0)
{
cnt = d1 + 1;
}
else
{
cnt = gcd(d1, d2) + 1;
}
if (cnt == k)
{
ans++;
}
}
}
}
}
cout << ans ;
}
|
C Right Triangles
给出$N$个点$(x,y)$,每个点与$(0,0),(x,0)$会形成一个直角三角形,问每一个直角三角形包含的三角形个数有多少个。
按x坐标排序,然后求前面有多少是斜率比自己小的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| int n;
struct no
{
int le;
int ri;
int id;
}node[maxn];
bool cmp(no a,no b)
{
return a.le<b.le;
}
ll num[maxn];
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
ll getsum(ll x)
{
ll ans = 0;
while(x>0)
{
ans+=num[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
ll add(int x,int v)
{
int up=maxn-1;
while(x<=up)
{
num[x]+=v;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
return x;
}
int ans[maxn];
void solve()
{
sa(n);
repp(i,1,n)
{
sa(node[i].le);
sa(node[i].ri);
node[i].id = i;
}
sort(node+1,node+n+1,cmp);
repp(i,1,n)
{
int k = getsum(node[i].ri-1);
ans[node[i].id] = k;
add(node[i].ri,1);
}
repp(i,1,n)
{
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
}
|
D Triangular Updates
给出一个矩形,每次都在一个直角三角形上操作,问最后的矩形数值。
想不出来。。。哭啊。。。
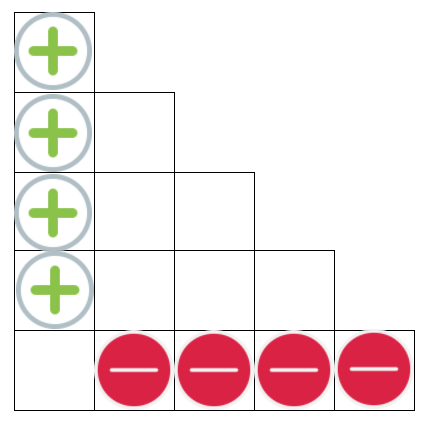
如图所示。。。这样更新就好了。。。。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| ll val[maxn][maxn];
ll val2[maxn][maxn];
ll ad[maxn][maxn],sub[maxn][maxn];
void solve()
{
int n,q;
sa(n),sa(q);
repp(i,1,q)
{
int R,C,L,S;
sa(R);
sa(C);
sa(L);
sa(S);
ad[R][C] += S;
ad[R+L][C] -= S;
sub[R+L][C+1] -= S;
sub[R+L][L+C+1] += S;
}
repp(i,1,n)
{
repp(j,1,n)
{
sub[i][j] += sub[i][j-1];
}
}
repp(j,1,n)
{
repp(i,1,n)
{
ad[i][j] += ad[i-1][j];
}
}
repp(i,1,n)
{
repp(j,1,n)
{
val[i][j] = ad[i][j] + sub[i][j];
if(i>1&&j>1)val[i][j] += val[i-1][j-1];
printf("%lld ",val[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
|
E Sliding Product Sum
题意是有一个$1$到$N$的数组$(N<10^18)$,计算里面小于等于K的连续子数组的乘积之和。
从1到n连续K个数的乘积之和为
$$
\frac{(n-i+1)(n-i+2)…(n+1)}{(i+1)}
$$
例如1*2 + 2*3 + 3*4 + 4*5 + … (n-1)*n = (n-1)*n*(n+1)/2
然后这题直接Python上。。。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
def cal(n,x):
ans = 1
for i in range(x + 1):
ans *= (n + 1 - i)
return ans / (x + 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n,m,k = map(int,raw_input().split())
ans = 0
for i in range(1,m+1):
ans += cal(n,i)
ans %= k
print ans
|
